

The Brinell hardness tester uses the oldest method of hardness testing still in widespread use. Developed in 1900 by Swedish engineer Dr. Johan August Brinell, this technique (standardized as ISO 6506 Brinell) is especially suited for measuring the hardness of castings and forgings with grain structures too rough for Rockwell or Vickers testing.
Brinell hardness test conditions have approximately 25 different load/ball combinations. This allows almost all metals to be tested using the Brinell hardness test (HBW) by simply varying the ball size and test force based on the sample’s dimensions and design. The concept is the same whether a digital Brinell hardness tester or a handheld Brinell hardness tester is used. In some cases, as long as the ball size to test the force ratio remains constant, the results are considered accurate when changing between Brinell test conditions.
The HBW Brinell scale (where “H” stands for hardness, “B” for Brinell, and “W” for a tungsten carbide ball) is the most commonly used variant, especially for ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Results from the Brinell hardness tester are used extensively in industry as a basis for commercial shipment acceptance and quality control. The hardness values obtained from the Brinell test can also provide insights into other material properties, including:
Our Brinell hardness testers can withstand the most harsh environments. If necessary, they can be used with an air filtration system to protect the interior against dust. The testers are available in various formats, including the portable Brinell hardness tester for on-site applications, as well as bench-mounted and floor-standing models for high-precision testing in lab or industrial settings.
INNOVATEST offers various dedicated Brinell hardness testers that are closed loop, loadcell-based machines. Our instruments are developed, designed and endurance tested at our R&D facilities, and offer our customers the choice between basic manual testing or fully automatic Brinell testing.
All instruments are equipped with user friendly, advanced IMPRESSIONS software which allows for ease of use, while accommodating for complex applications and workflows. In addition, all critical internal electronic components are manufactured by INNOVATEST, allowing for a high level of manufacturing quality control, and ensuring a reliable hardness testing instrument for many years, backed by our extended warranty options.
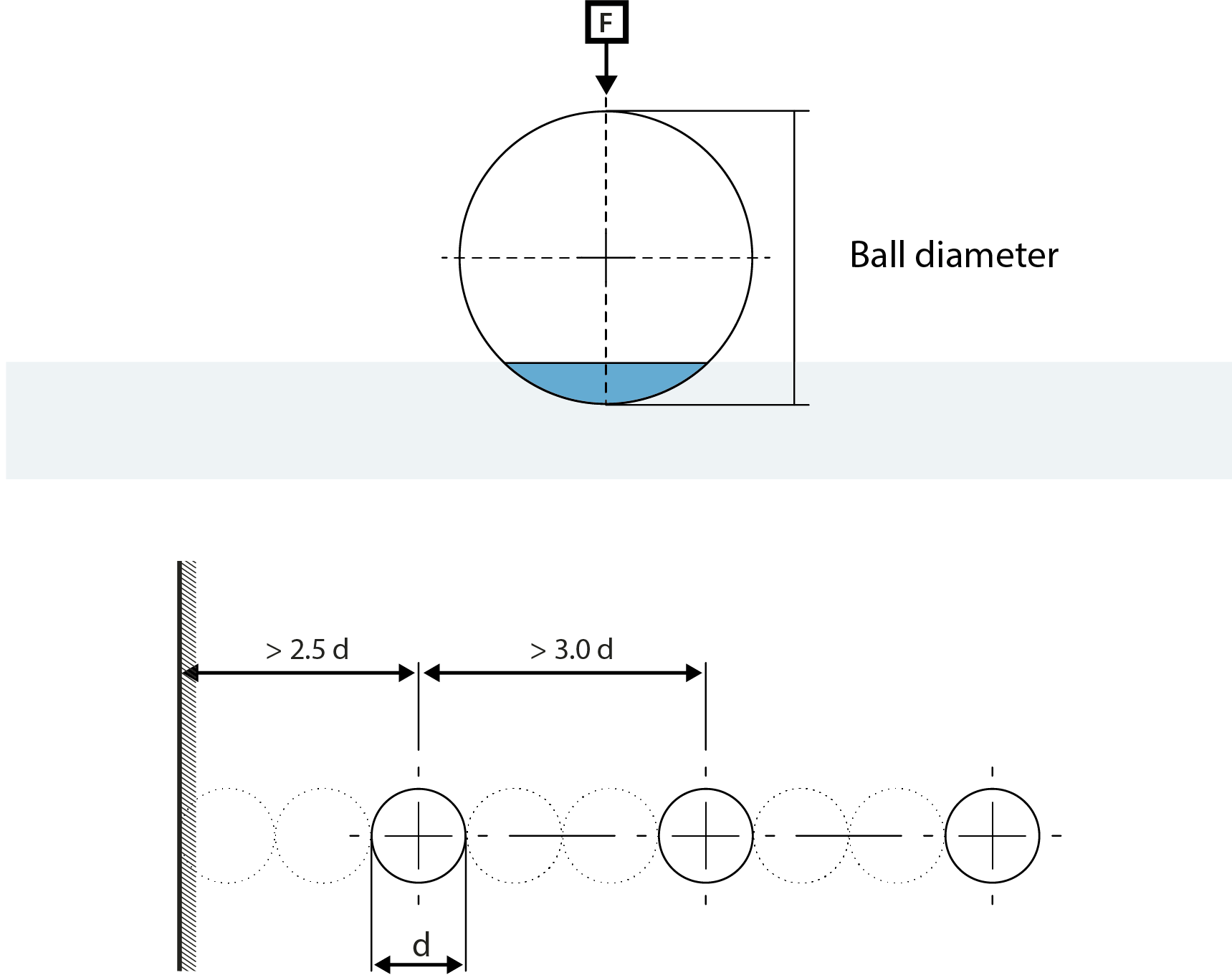
The Brinell test can be simply explained as an indentation hardness test consisting of two basic steps.
Step 1: Indentation
Step 2: Measurement

The Brinell hardness test (HBW) uses a tungsten carbide ball as the indenter and applies a specified load to measure material hardness. “HBW” is the standard designation in this method, where “W” refers to the tungsten carbide material of the ball.
ISO 6506 is the international standard that outlines the procedures and requirements for performing Brinell hardness testing on metallic materials. It covers the use of different ball sizes, test loads, and the calculation of hardness values.
The Brinell hardness test is performed using a specialized machine called a Brinell hardness tester. It uses a steel or tungsten carbide ball to indent the material under a specific load, then measures the diameter of the indentation to calculate the Brinell Hardness Number (BHN).
Brinell hardness is tested by pressing a hard ball into the surface of a material using a known force for a set dwell time. The diameter of the resulting indentation is measured, and the Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) is calculated using a standard formula.
A Brinell hardness tester measures the resistance of a material to indentation. It helps determine material properties like strength and wear resistance.
The minimum recommended thickness for Brinell hardness testing is 8 times the depth of the indentation. This minimum requirement is set to ensure the test base does not affect the test results.
Typical steels have a Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) ranging from 120 to 600, depending on the grade and heat treatment. For example, mild steel is around 120–180 BHN, while hardened tool steels can range from 600–900 BHN.